Supply Chain Risk
October 28, 2011 2 Comments
The current flooding in Thailand, the worst for fifty years, is showing the importance of supply chain risk management. The country has been devastated by monsoon rains and this is now starting to affect Bangkok. A number of major manufacturers, such as Toyota have plants in Thailand (Samrong, Gateway and Ban Pho) and these manufacturers have experienced difficulties. The Toyota plants have not been directly affected by the flooding, however they have been indirectly affected as a result of part supply delays which have resulted in production in all three plants being stopped. Due to the global nature of supply chains the flooding has not just stopped operations in Thailand it has effected operations in Japan with Toyota being unable to get raw materials from Thailand.
Such global supply chains are a source of competitive advantage allowing firms to gain the advantage of cheap labour, cheap raw material, local expertise and government incentives but such global supply chains can increase supply chain risk. Risk has many definitions:-
- it is the combination of the probability of events and its consequences
- it is the effect of uncertainty on objectives
- it is often characterised as what can happen, the likelihood of it happening and the consequences of it happening (similar to a FMEA)
So what can be done to reduce this risk, and how are supply chain trends affecting supply chain risks?
Supply Chain trends
A number of supply chain trends can be identified which have influenced the level of risk in our supply chains, these trends are well reported in the media but the negative side of such trends are often ignored. The key trends are:-
- Lean supply chains and JIT. This focus on efficiency rather than effectiveness has led to increased supply chain vulnerability as capacity and inventory is removed
- Reducing costs through globalised supply chains. This has led to longer supply chains which are more complex and more vulnerable to disruptions
- Reduced costs through economies of scale (centralisation). This has reduced cost and flexibility in the supply chain
- Reduced costs through outsourcing. This has led to a loss of management control of the supply chain
- Reduced costs through consolidation of suppliers. This has increased the chance of supply chain disruption.
How can risk be categorised?
There are four areas of supply chain risk:-
- Supply
- Demand
- Operational
- Security
These areas can be further divided based upon the likelihood of the event and the consequences of the event e.g. low likelihood, high consequences. Studies have shown that companies work hard to reduce recurrent risks in their supply chain (such as currency risks) but do little to reduce the impact of high impact low likelihood events such as natural disasters. However, such environmental disasters seem to be occurring more often this means that such attitudes need to change and companies need to start to develop plans to reduce the effect of unpredictable events.
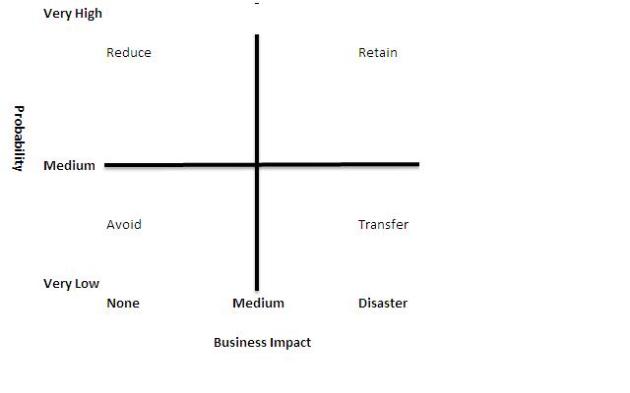
A number of risk management strategies have been developed which depend on the probability of an incident and the effect on the business, these are shown on the diagram below
Low Business Impact
Avoid = Proactive action which removes the event
Reduce =Action reduces the effect of an event if it occurs
High Business Impact
Transfer = Proactive action which switches risk to 3rd party
Retain = Reduces the impact if event occurs
What tactics can be used?
A variety of tactics may be applicable:-
Reactive
- Change product configuration to cope with disruption
- Change supply plan to cope with disruption
- Change pricing to satisfy customers and use promotions to switch demand to products that you do have
Proactive
- Postponement – modular designs allow switching to other components
- Use more than one supplier as it adds flexibility (often means guaranteeing orders to keep business running)
- Resilient supply chain design
- Flexible transportation routes
So how should you manage your risk?
- Understand the end to end supply chain
- Reduce complexity in the supply chain
- Identify bottlenecks & key nodes and develop plans to cope with disruption
- Establish continuity plan & team
- Share information and work with customers / suppliers